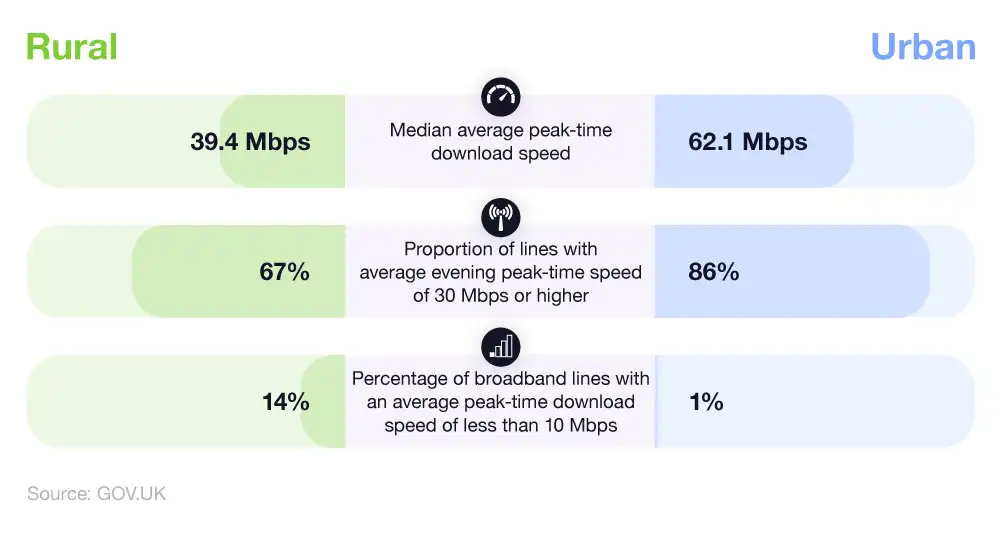
If you are living in a rural area then you’ll know that getting fast and reliable broadband can be tough. According to a post by Uswitch, there is a significant difference between urban and rural average wifi speeds. The average broadband speed for someone living in an urban environment is 61.2mbps and the average for a rural area is 39.4mbps (source). Another stat is that 16% of those in rural areas with broadband have a speed of 10mbps or less, compared to only 1% in urban areas.
Why is rural broadband often so slow?
Types of broadband available in rural locations
Rural ADSL and fibre broadband
Mobile broadband for rural locations
Satellite broadband for rural homes
Why is rural broadband often so slow?
Slow rural broadband in the UK can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Infrastructure Challenges: One of the primary reasons for slow rural broadband is the lack of adequate infrastructure. Rural areas often have lower population densities, making it less economically viable for internet service providers (ISPs) to invest in the necessary infrastructure to provide high-speed broadband.
- Distance from Exchange Points: Rural areas are typically located farther away from exchange points where internet connections are routed. This increased distance can result in signal degradation and slower speeds, especially with traditional copper-based networks.
- Limited Investment: Historically, ISPs have focused their investments on urban and densely populated areas where the potential return on investment is higher. As a result, rural areas have been neglected, leading to outdated or inadequate broadband infrastructure.
- Topography and Geography: The geographical layout of rural areas, such as hills, valleys, and remote terrain, can pose challenges for installing broadband infrastructure. These physical barriers can make it difficult and expensive to lay cables or erect towers for wireless connectivity.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Regulatory processes and bureaucratic red tape can delay or deter ISPs from expanding their networks into rural areas. Obtaining permits and approvals for infrastructure development in rural regions may be more complex and time-consuming compared to urban areas.
- Cost Constraints: Providing broadband services to rural areas involves higher costs per household due to the need for extensive infrastructure deployment over larger distances. This can make it financially unfeasible for ISPs to offer affordable high-speed internet to rural communities.
- Limited Competition: In many rural areas, there may be limited competition among ISPs. Without competition driving innovation and investment, there is less incentive for ISPs to improve broadband speeds or expand coverage in these areas.
- Technological Limitations: Some rural areas may still rely on outdated technologies like ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) or satellite internet, which offer slower speeds compared to newer technologies like fiber-optic broadband.

Addressing the issue of slow rural broadband in the UK requires a multifaceted approach involving government intervention, private sector investment, and community initiatives to bridge the digital divide and ensure equitable access to high-speed internet for all citizens.
Types of broadband available in rural locations
The type of broadband you can get really depends on your location. You might be lucky and have traditional fibre or wired broadband available. A good way to check what type of broadband you can get is by using Go Compare, they have tool specifically for rural broadband.
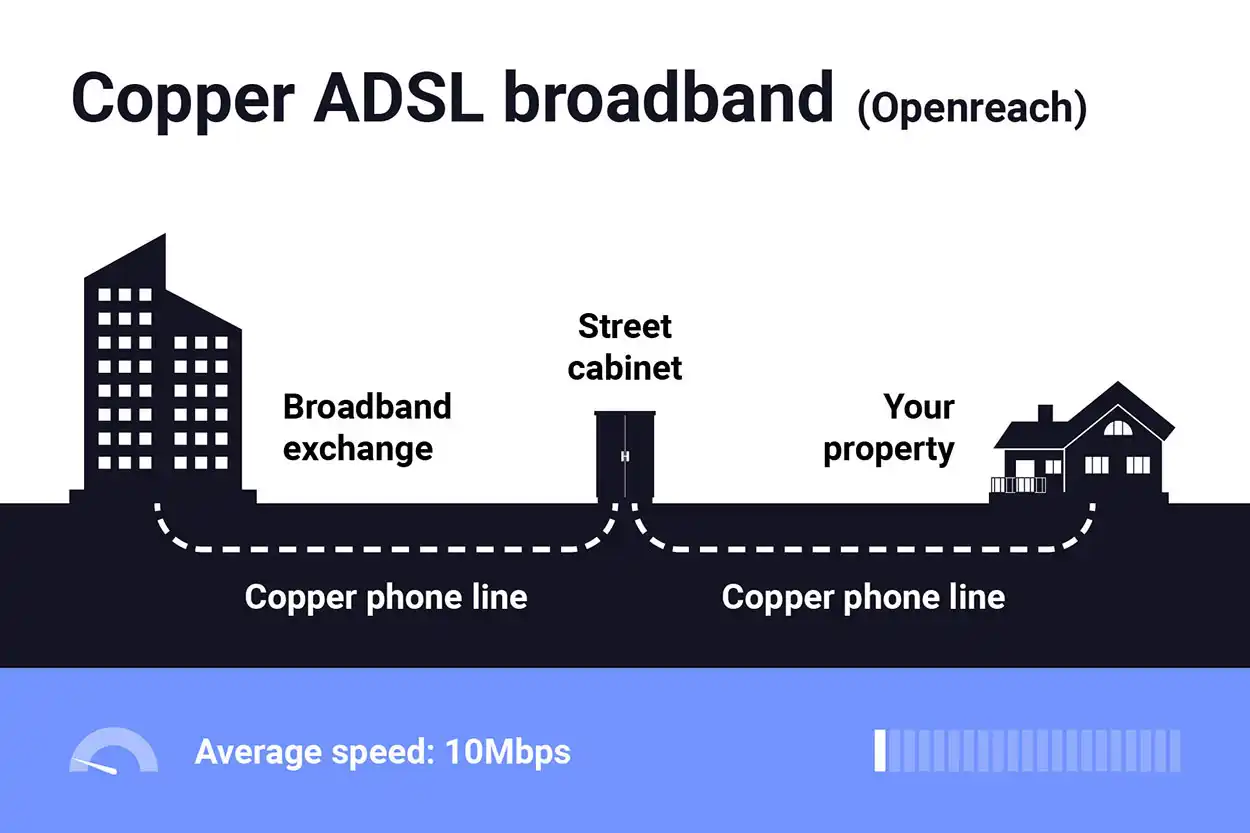
ADSL is one of the most widely available types of broadband in rural areas. It utilises existing telephone lines to deliver internet access, making it relatively easy to deploy. However, ADSL speeds can be limited, especially the further away a location is from the telephone exchange.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): FWA provides broadband access using wireless technology, typically via radio signals transmitted from a fixed base station. This technology is well-suited for rural areas where laying cables or fiber-optic infrastructure may be impractical or cost-prohibitive. FWA can offer faster speeds than ADSL but may still be limited by factors such as signal interference or obstructions.
Satellite Internet: Satellite internet involves sending and receiving data via satellites orbiting the Earth. It is available virtually everywhere, including rural and remote locations where other types of broadband may not reach. While satellite internet offers broad coverage, it can be more expensive and suffer from latency issues due to the long distance data must travel between Earth and satellites.
Rural ADSL and fibre broadband
In rural areas, accessing reliable and high-speed internet can be a challenge, with residents often limited to traditional technologies like ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) or, in some fortunate cases, emerging options like fiber broadband. Let’s delve into the characteristics of both to understand their impact on rural connectivity.
ADSL in Rural Areas:
ADSL remains a common broadband option in rural regions due to its relatively widespread availability and ease of deployment. You can read more about ADSL broadband on the Go Compare website here. Here’s what you need to know about ADSL in rural settings:
- Utilization of Existing Infrastructure: ADSL relies on the existing copper telephone lines, which are often already in place in rural areas. This makes it a convenient option for ISPs to extend broadband services to these regions without significant infrastructure investment.
- Limited Speeds and Reliability: While ADSL can provide basic internet access, its speeds are often limited, especially for locations far from the telephone exchange. Rural residents may experience slower connections and less reliable service compared to urban counterparts.
- Distance Limitations: The speed and quality of ADSL connections degrade with distance from the telephone exchange. In rural areas where exchanges are few and far between, this distance factor can significantly impact broadband performance, leading to slower speeds and potential signal interference.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Despite its limitations, ADSL can still be a cost-effective solution for rural areas where alternatives like fiber broadband may not be feasible. Its affordability makes it accessible to communities with limited budgets or where population densities are low.
Source (https://www.uswitch.com/broadband/guides/quick-guide-to-adsl/)
Fiber Broadband in Rural Areas:
Fiber optic broadband represents the gold standard in internet connectivity, offering unparalleled speed and reliability. While less common in rural areas, fiber broadband is gradually expanding. Here’s what makes it noteworthy:
- High-Speed Connectivity: Fiber optic cables transmit data using light signals, enabling significantly faster internet speeds compared to ADSL. Rural communities fortunate enough to have access to fiber broadband can enjoy blazing-fast connections, suitable for bandwidth-intensive activities like HD streaming, online gaming, and remote work.
- Reliability and Stability: Fiber optic connections are less susceptible to environmental factors and signal degradation, offering a more stable internet experience. This reliability is particularly beneficial in rural areas where inclement weather or geographical challenges can affect traditional broadband services.
- Limited Availability and Deployment Challenges: Despite its advantages, fiber broadband deployment in rural areas faces hurdles such as high infrastructure costs and logistical challenges. Layings fiber optic cables across vast, sparsely populated regions can be prohibitively expensive, leading to slower adoption rates compared to urban areas.
- Future-Proof Infrastructure: Investing in fiber optic networks lays the groundwork for long-term connectivity solutions in rural communities. While the initial costs may be high, fiber broadband offers scalability and future-proofing, ensuring that rural areas remain competitive and connected in the digital age.
While rural ADSL and fiber broadband serve as vital connectivity lifelines for rural communities, there’s a clear disparity in performance and reliability. While ADSL remains a pragmatic choice for many rural areas, fiber broadband represents the ideal solution for unlocking the full potential of rural connectivity, offering unparalleled speed, reliability, and future-proof infrastructure. Bridging the gap between these technologies requires concerted efforts from governments, ISPs, and community stakeholders to ensure equitable access to high-speed internet for all rural residents.
Mobile Broadband in Rural Areas
In rural areas where traditional fixed-line broadband options like ADSL or fiber are limited, mobile broadband emerges as a viable solution to bridge the digital divide. Let’s explore the characteristics of mobile broadband and its impact on rural connectivity:
Mobile Broadband Overview:
- Utilization of Cellular Networks: Mobile broadband leverages cellular networks to deliver internet connectivity to users. This technology allows rural residents to access the internet via their smartphones, tablets, or dedicated mobile broadband devices.
- Broad Coverage: One of the key advantages of mobile broadband is its broad coverage, extending to even the most remote and sparsely populated areas where deploying fixed-line infrastructure may be impractical or cost-prohibitive.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Mobile broadband offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing users to access the internet on the go. This mobility is particularly beneficial for rural residents who may need internet access outside of their homes, such as while traveling or working in the field.
- Variable Speeds and Reliability: While mobile broadband can offer decent speeds, especially in areas with good network coverage, the actual performance may vary depending on factors such as network congestion, signal strength, and geographical features. Rural residents may experience slower speeds and less reliable connections, particularly in areas with limited network infrastructure.
- Data Caps and Fair Usage Policies: Many mobile broadband plans come with data caps or fair usage policies, which can limit the amount of data users can consume within a given billing cycle. In rural areas where fixed-line alternatives are scarce, mobile broadband may be the primary option despite these limitations.
Mobile networks provide broadband connectivity through a combination of radio signals, cellular towers, and network infrastructure. There’s a lots of providers available, where you can purchase some kind of “hub” which basically works as a router/modem. You can find a list of the best mobile network broadband providers by expert reviews here.
Considerations for Rural Mobile Broadband:
- Network Coverage and Quality: Before opting for mobile broadband in rural areas, it’s essential to assess the coverage and quality of available networks. While major carriers often prioritize urban areas, some providers offer specialized rural coverage plans or utilize technologies like satellite backhaul to extend coverage to underserved regions.
- Equipment and Devices: Rural residents may need to invest in compatible mobile broadband devices such as smartphones, tablets, or mobile hotspot routers to access mobile internet services. Additionally, external antennas or signal boosters may be necessary to improve reception in areas with weak signals.
- Usage Patterns and Needs: Understanding your internet usage patterns and needs is crucial when choosing mobile broadband plans. Heavy internet users or households with multiple devices may require higher data allowances to avoid exceeding monthly caps or incurring additional charges.
- Complementary Solutions: In some cases, combining mobile broadband with other connectivity solutions such as satellite internet or community networks can provide a more robust and reliable internet experience in rural areas. Exploring hybrid or complementary approaches tailored to specific community needs can help address connectivity challenges more effectively.
Obedio is a multi-faceted organisation that specialises in internet and communication solutions for commercial, domestic and personal use. Notspot is here to help your or your business get wifi in rural areas. Please get in touch with us today using this link! You can find out more information about broadband in rural areas by reading our blog post The Ultimate Guide to Getting Broadband in Rural Areas: Solutions and Tips.

