In today’s digital age, a strong WiFi connection is essential for smooth internet browsing, streaming, gaming, and more. However, many of us struggle with dead zones or weak signals in certain areas of our homes. But fear not! With a few simple techniques and tweaks, you can Boost Your WiFi Signal Strength and coverage, ensuring a seamless online experience throughout your home.
Here at Notspot Broadband we are experts in all things broadband and wifi, with over 30 years of experience. Get in touch if you need help with getting fast and reliable broadband to your home or business. Even in the most rural areas of the UK we are connecting Homes and Businesses like your’s every day!
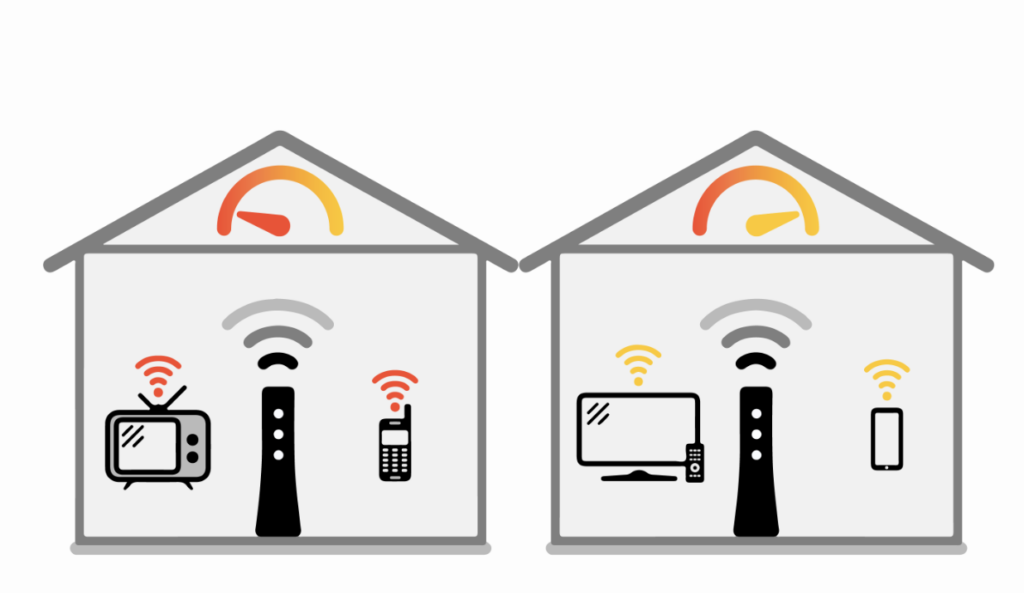
What is WiFi Signal Strength?
WiFi signal strength, often measured in decibels milliwatt (dBm), indicates the power level of the wireless signal transmitted by your router. It represents the intensity of the radio waves traveling between your router and your device, such as a smartphone, laptop, or smart TV. A stronger signal means better connectivity and faster data transfer rates, while a weaker signal may result in slower speeds, dropped connections, or intermittent interruptions.
Factors Affecting WiFi Signal Strength
Several factors can influence WiFi signal strength, including:
-
- Distance from the Router: The farther you are from your router, the weaker the WiFi signal becomes. Walls, floors, and other obstructions can also attenuate the signal, further reducing its strength.
-
- Physical Obstacles: Thick walls, metal objects, and electronic appliances can block or interfere with WiFi signals, leading to signal degradation and dead zones within your home.
-
- Interference from Other Devices: Nearby electronic devices operating on the same frequency band, such as cordless phones, microwave ovens, and Bluetooth devices, can cause interference and weaken your WiFi signal.
-
- Router Placement: The placement of your router plays a crucial role in signal strength. Positioning your router in a central location within your home and elevating it off the ground can help maximise signal coverage.
Measuring WiFi Signal Strength
WiFi signal strength is typically measured using a metric called Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), expressed in dBm. RSSI values range from 0 dBm (strongest signal) to -100 dBm (weakest signal). Most devices display signal strength bars, with more bars indicating a stronger signal.
Interpreting WiFi Signal Strength
Understanding WiFi signal strength readings can help you optimize your network performance:
-
- Excellent Signal (-30 to -50 dBm): Indicates a very strong signal with excellent connectivity and maximum data transfer speeds.
-
- Good Signal (-51 to -70 dBm): Represents a good signal with reliable connectivity and high data transfer rates.
-
- Fair Signal (-71 to -90 dBm): Indicates a fair signal strength, which may result in slower speeds and occasional connectivity issues.
-
- Weak Signal (-91 to -100 dBm): Represents a weak signal with poor connectivity and slow data transfer rates. Users may experience frequent disconnections and sluggish performance.
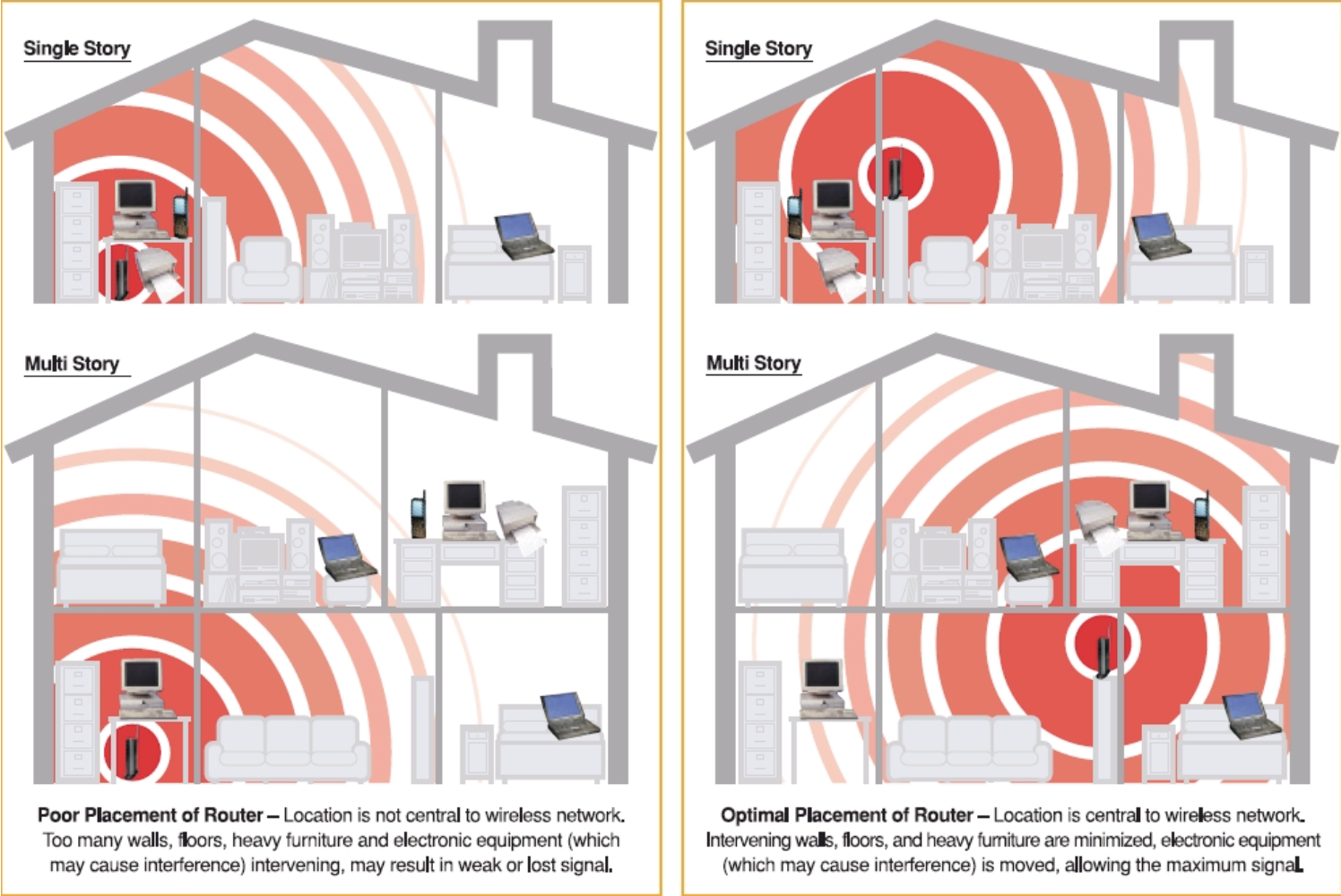
Optimise Router Placement
The placement of your WiFi router plays a crucial role in the strength and coverage of your WiFi signal. Place your router in a central location within your home, away from obstructions such as walls, furniture, and electronic devices that can interfere with the signal. You can easily get a good understand of how good your placement is by moving around your home or business and see how many bars on your device display, the more bars, the better the connection.
Update Router Firmware
Keep your router’s firmware up to date to ensure optimal performance and security. Manufacturers often release firmware updates that include improvements to signal strength and overall performance. This blog post explains this in more detail, How to update your router’s firmware (and why you should be doing it regularly).
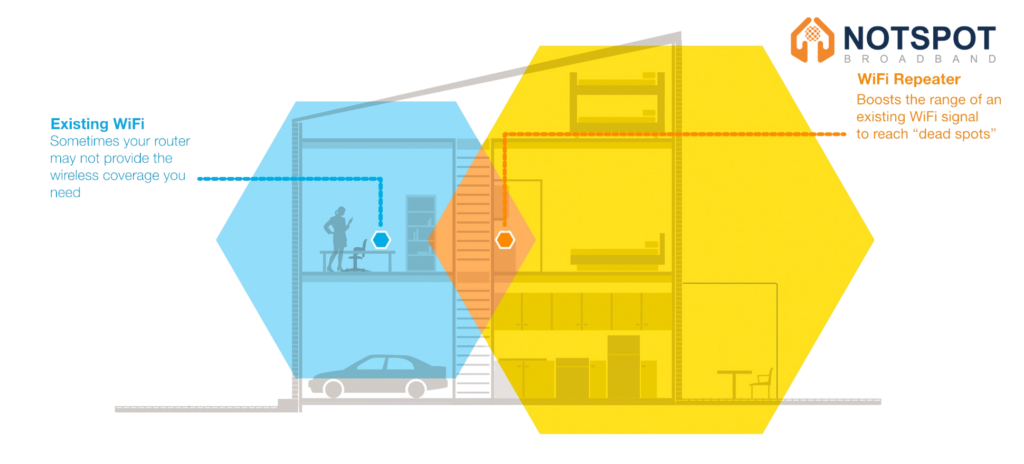
Use WiFi Range Extenders
WiFi range extenders, also known as WiFi boosters or repeaters, can help amplify your WiFi signal and extend its coverage to areas with weak or no reception. Place range extenders strategically between your router and areas with poor signal to bridge the gap and improve coverage. Follow the link for a list of the best Wifi ranger extenders in 2024 provided by PC Mag.
Invest in a Mesh WiFi System
A mesh WiFi system consists of multiple interconnected nodes that work together to create a single, seamless WiFi network with consistent coverage throughout your home. This solution is particularly effective for larger homes or spaces with multiple floors. PC Mag has provided a list of the best Mesh Wifi systems available in the UK for 2024, click here to view it.
Secure Your Network
Securing your WiFi network not only protects your data but also ensures that unauthorised users aren’t leeching off your bandwidth, which can degrade your connection speed. Use strong, unique passwords for your WiFi network and consider enabling network encryption such as WPA2.
How to secure your home wifi network
Securing your home WiFi network is paramount to safeguarding your privacy, data, and personal information from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Here are some essential steps to ensure the security of your WiFi network:
1. Change Default Network Name (SSID) and Password: Most routers come with default network names (SSIDs) and passwords, which are often easy to guess or commonly known. Change both the SSID and password to unique, strong combinations that are difficult for others to guess. Avoid using personal information in your SSID or password.
2. Enable Network Encryption: Encrypting your WiFi network prevents unauthorized users from intercepting and deciphering your data. Use the latest encryption protocol supported by your router, such as WPA2 (WiFi Protected Access 2) or WPA3, to encrypt your network traffic. Avoid using outdated and less secure encryption methods like WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy).
3. Implement Strong Passwords: Choose strong, complex passwords for both your WiFi network and router administration interface. A strong password typically consists of a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Regularly update your passwords and avoid using easily guessable phrases or common dictionary words.
4. Enable Network Firewalls: Most modern routers include built-in firewall capabilities to filter incoming and outgoing network traffic. Enable the router’s firewall and configure it to block unauthorized access attempts and filter potentially harmful content. Additionally, consider installing reputable firewall software on your devices for an extra layer of protection.
5. Disable WPS (WiFi Protected Setup): While convenient for easy device connection, WPS can pose a security risk as it may be vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Disable WPS on your router to prevent unauthorized users from exploiting this vulnerability to gain access to your network.
6. Enable MAC Address Filtering: MAC (Media Access Control) address filtering allows you to specify which devices are allowed to connect to your WiFi network based on their unique MAC addresses. While not foolproof, MAC address filtering adds an additional layer of security by restricting access to authorized devices only.
7. Regularly Update Router Firmware: Keep your router’s firmware up to date by installing the latest security patches and updates released by the manufacturer. Regular firmware updates help address known vulnerabilities and strengthen the overall security of your router against emerging threats.
8. Disable Remote Management: Disable remote management features on your router unless absolutely necessary. Remote management can potentially expose your router to unauthorized access from the internet, increasing the risk of security breaches.
Reduce WiFi Interference
Minimise interference from other electronic devices by positioning your router away from devices like cordless phones, microwaves, and Bluetooth speakers. Additionally, consider switching to less crowded WiFi channels to reduce interference from neighbouring networks.
Upgrade Your Router and Antennas
If you’re still using an older router, consider upgrading to a newer model that supports the latest WiFi standards, such as 802.11ac or 802.11ax (WiFi 6). Additionally, you can enhance your router’s signal strength by upgrading its antennas to high-gain antennas.
Conclusion: Boost Your WiFi Signal Strength
By following these simple tips and tricks, you can boost your WiFi signal strength at home and enjoy a faster, more reliable internet connection. Whether you’re streaming your favorite shows, gaming with friends, or working from home, a strong WiFi signal is key to a seamless online experience.
Implement these strategies today and say goodbye to WiFi dead zones and weak signals once and for all!
If you need to get a better broadband connection and faster wifi in rural areas, get in touch with Notspot Broadband today!